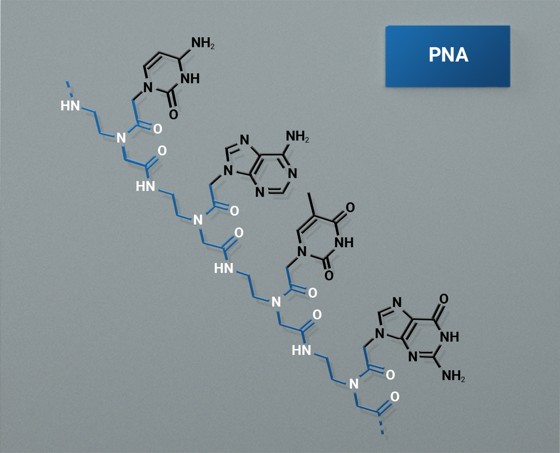
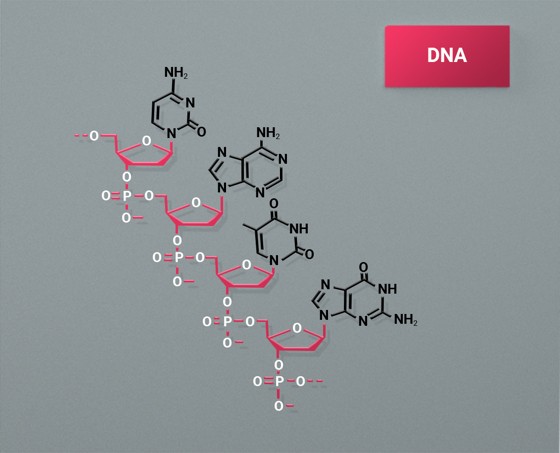
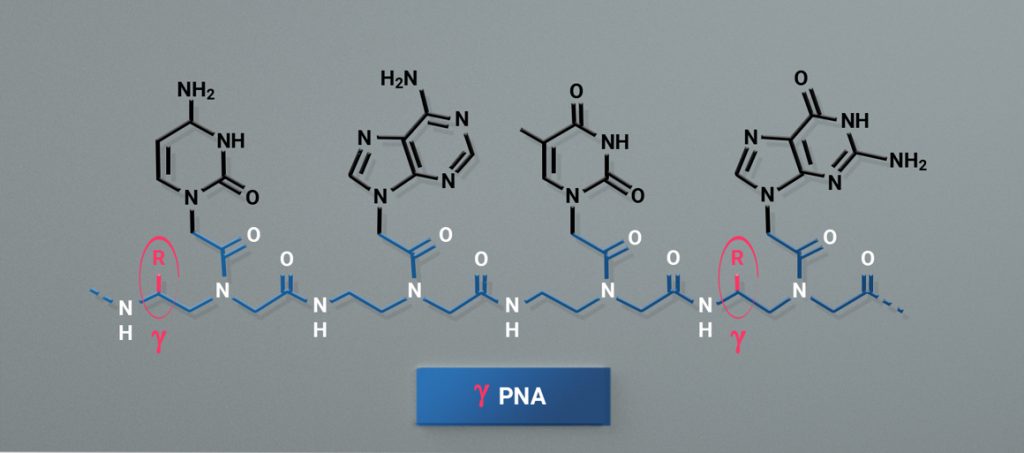
Standard PNAs are composed of acyclic, achiral, and uncharged pseudopeptide backbones, which differ significantly from conventional DNA structures in which the sugar phosphate groups are repeatedly substituted with N-(). 2-Aminoethyl)glycine units are replaced.
This unique structure gives PNAs several distinct advantages over conventional DNA and RNA molecules. One of these advantages is their remarkable chemical stability. Unlike DNA, PNA is highly resistant to enzymes such as nucleases and proteases that normally degrade DNA and RNA. This resilience gives PNAs long-term durability, which may be important in a variety of research and clinical settings.
Another important advantage of PNAs is their strong binding affinity to complementary DNA and RNA sequences. This binding occurs via standard Watson-Crick base-pairing, which allows PNAs to form highly stable duplex structures with DNA and RNA, even under conditions of low ionic strength. will be In addition, PNA-DNA and PNA-RNA duplexes are less susceptible to RNAse H cleavage, further enhancing their stability.
The neutral backbone of PNA also confers unique hybridization properties, resulting in significantly higher thermal stability compared to DNA-DNA duplexes when bound to complementary nucleic acids. This high thermal stability and lack of charge in PNAs allows for more accurate and powerful probes, improving detection and quantification of specific target sequences.
Furthermore, PNA binds to double-stranded DNA through strand invasion, breaking the DNA duplex and forming a highly stable PNA-DNA complex. This is especially useful for gene editing and targeted sequencing applications that require high sequence specificity and cannot be done with natural nucleic acid strands.
Finally, the unique biochemistry of PNAs opens up possibilities for further modifications and functionalizations such as: B. Attachment of fluorophores, quenchers, or other reporter groups. This makes it a versatile tool in the fields of diagnostics, therapeutics, and biotechnology.
In summary, PNAs are excellent alternatives to DNA and RNA in many applications due to their superior stability, strong binding affinity, high sequence specificity, and versatile adaptability. These properties make custom PNAs important players in the development of advanced techniques for nucleic acid detection and manipulation.